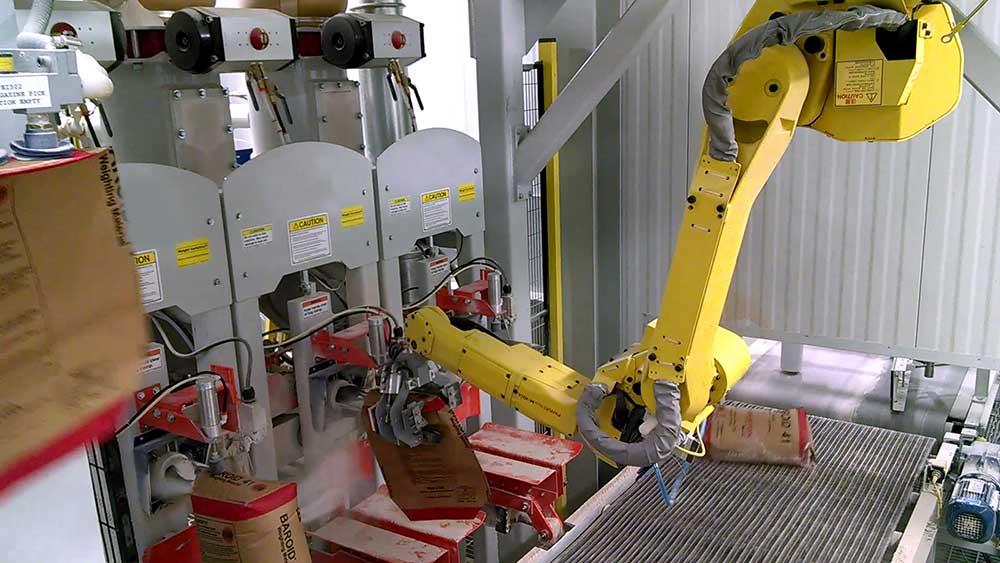
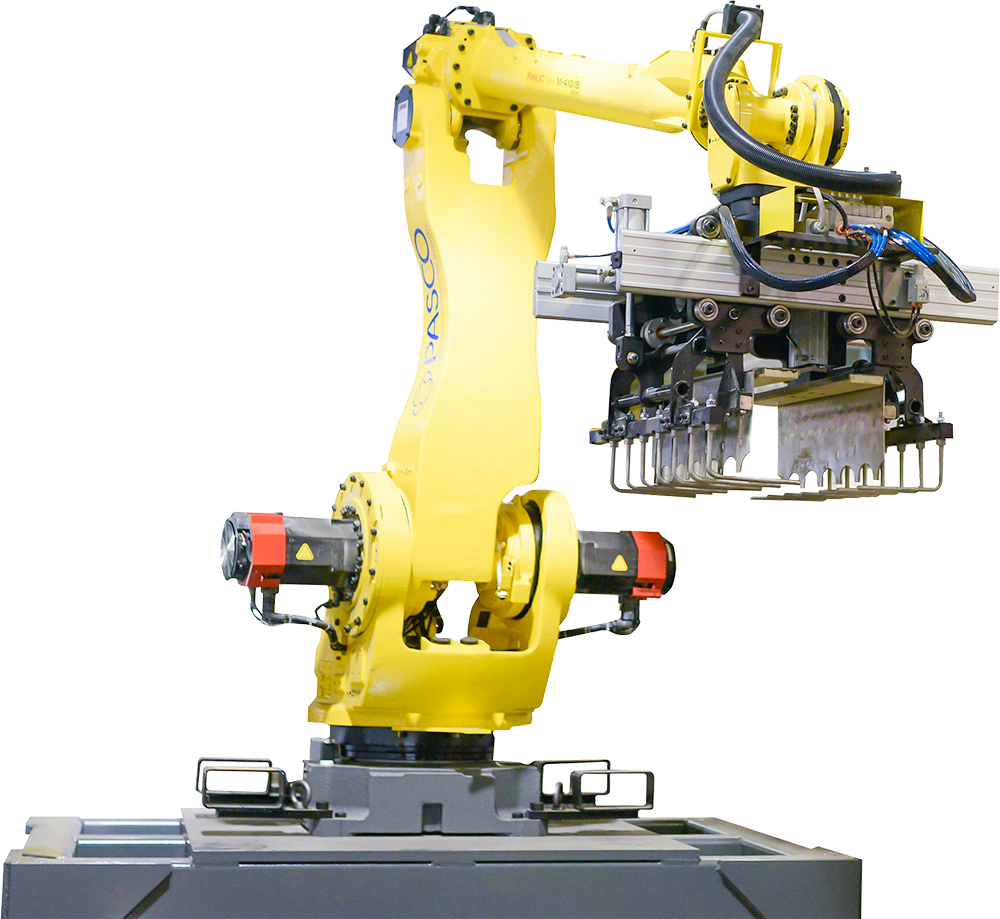
Valve bag placement plays a direct role in your plant’s efficiency, product quality and operator safety. When the process is manual, it relies on human labor to pick, open and position bags on a filler spout — a setup that often leads to slowdowns and inconsistent results.
Robotic valve bagging changes that equation. Systems like PASCO’s robotic valve bag placer deliver high-speed, repeatable performance that minimizes downtime and improves reliability across shifts.
This guide breaks down the hidden costs of manual valve bagging, lays out what goes into a modern robotic valve bagging system and walks through integration, real-world use cases and where the technology is heading.
WHAT ARE THE HIDDEN COSTS AND RISKS OF MANUAL VALVE BAG PLACEMENT?
In a manual setup, workers place each valve bag by hand — picking the bag, opening it, lining it up and fitting it onto the spout until its full, then removing the bag and ensuring its closed. It gets the job done, but not without hidden costs: labor, strain, slowdowns and mistakes that add up.
How does labor intensity impact manual valve bagging operations?
Manual valve bagging means workers are lifting 25–50 lb bags over and over, bending, and lining them up on the spout with precision. Over time, that takes a toll:
- Repetitive strain injuries like carpal tunnel or tendonitis from constant gripping
- Back and joint problems from the weight and awkward movements
- Fatigue and burnout that drive turnover and raise training costs
- Powder exposure that creates respiratory risks and adds to housekeeping demands
The strain on people makes a strong case for automation not just to protect workers, but to keep production running smoothly without interruption.
Ergonomic risks of manual bagging
Manual valve bagging often leads to repetitive strain injuries and musculoskeletal disorders due to the physical demands of lifting and positioning heavy bags. These injuries can result in reduced worker morale and increased costs associated with employee turnover and training.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), “Ergonomic Guidelines for Manual Material Handling” (2018)
This research supports the article’s claims about the ergonomic challenges of manual valve bag placement and the benefits of automation in reducing these risks.
What inconsistencies and product waste arise from manual bagging?
When bags are placed by hand, orientation and seal alignment aren’t always consistent. That’s when problems creep in:
- Misaligned bags that create leak points and release dust
- Bags not fully opened, leading to bad fill weights or overfilling
- Spills and dust that waste product and drive up cleanup costs
All of this adds up to higher waste and quality issues, one of the biggest reasons companies turn to robotic placement for accuracy they can count on.
How do speed limitations affect manual valve bagging productivity?
A skilled operator might keep up with 6–8 bags a minute when everything’s going right. But once fatigue sets in, that pace usually slips closer to 4 bags a minute. By comparison:
Machines don’t slow down. Robotic systems keep throughput steady and near-continuous, removing the limits of human speed and setting the stage for real automation gains.
WHAT ARE THE KEY ADVANTAGES OF ROBOTIC VALVE BAG PLACEMENT?
Robotic valve bag placement uses vision systems, end-of-arm tooling and motion control to pick and place empty bags without an operator touching them. In this section, we’ll break down how the technology works, the benefits it delivers and the value companies are seeing in real production.
How does robotic automation increase speed and throughput?
Robotic systems can place 15–20 bags a minute and they don’t tire out. With 24/7 availability, they keep production moving.
A few things make that possible:
- Optimized pick-and-place movements that reduce wasted motion and cycle time
- Precision grippers that open and place each bag without manual adjustment
- Continuous cycles with short maintenance windows that deliver more than 95% uptime
Robotic automation and throughput
Robotic systems move bags a lot faster than people can, and they don’t lose consistency over time. By following optimized motion paths with precision grippers and nonstop cycles, they keep production running at a higher, steadier rate, driving real gains in output.
Robotics Industries Association (RIA), “Robotics Market Report” (2022)
This source backs up the article’s point: robotic valve bag placement runs three times faster than manual labor. That kind of efficiency compounds quickly, helping plants hit production targets sooner and keep schedules on track.
What cost savings and ROI can be achieved with robotic systems?
utomation cuts costs across the board. Typical annual savings include:
- Labor: 2–3 full-time positions reallocated
- Waste: 20–50% reduction in spillage and rework
- Energy: Lower utility use from consistent cycle times
Most facilities see payback within 12–24 months, with savings continuing to grow over the long term.
Cost savings and ROI with automation
Automated packaging systems save money in three big ways: less labor, less waste and lower energy use. Those gains add up fast — most plants see payback in 12–24 months and the savings keep driving profitability long after.
Association for Packaging and Processing Technologies (PMMI), “The State of the Packaging Industry” (2023)
This citation provides industry data to support the article’s claims about the cost savings and return on investment achievable with robotic systems.
How does automation enhance workplace safety and ergonomics?
Robotic placement takes the heavy lifting and repetitive strain off workers. Built-in safeguards make the process safer all around:
- Enclosed cells keep dust contained and away from operators
- HMI access points lets operators manage systems from a safe distance
- Ergonomic relief shifts physical tasks to robots, cutting down on injuries and claims
The result is a healthier workforce and fewer costs tied to workplace injuries.
In what ways does robotic placement improve product quality?
Robotic precision means every bag is placed the exact same way, every time. That level of control drives major quality gains:
- Valve alignment within 0.1 mm keeps fill weights consistent
- Stronger, more reliable seals cut leaks by more than 90%
- Defect rates drop from around 5% by hand to under 1% with robots
How flexible are robotic systems for different valve bag types?
PASCO valve bag placers are built to handle the variations that plants deal with every day, including:
- Bag sizes up to 100 lbs
- Handles both paper and plastic valve bags
WHAT ARE THE ESSENTIAL COMPONENTS OF A ROBOTIC VALVE BAG AUTOMATION SYSTEM?
A complete automation line comprises interlinked equipment that handles bags from magazine to pallet. Understanding each element aids in system design.
What features define robotic valve bag placers?
PASCO’s robotic valve bag placers combine:
- Six-axis robotic arm: Provides reach and dexterity.
- Vertical bag magazine: Stores bags for continuous feed.
- End-of-arm tooling: Grippers open and position the bag.
Which types of automated valve bag fillers are available?
Automated fillers deliver bulk material into the valve bag. Common types:
- Auger filler: Ideal for powders (cement, flour).
- Impeller filler: Handles granules (fertilizer).
- Air-powered filler: Suited for fragile flakes.
How do robotic palletizing systems integrate with bagging?
After filling, robotic palletizers take over to stack bags efficiently and securely. They coordinate handoff with conveyors, build stable layer patterns through programmed motions, and deliver high-speed handling — up to 64 bags per minute for 5, 7, and 10-lb bags, and up to 27 per minute for 50-lb bags.
What role do integrated control and conveyor systems play?
A central PLC orchestrates:
- Robot motion sequences
- Filler actuation
- Conveyor speeds
WHICH INDUSTRIES BENEFIT MOST FROM ROBOTIC VALVE BAG AUTOMATION?
Robotic valve baggers serve diverse sectors where bagging precision and speed are critical.
How does automation improve cement and building materials packaging?
In cement facilities, automated bagging:
- Handles abrasive powders without bag tears.
- Delivers 15–22 bags per minute consistently.
- Reduces dust emissions via enclosed filling.
What are the advantages for chemical, mineral and fertilizer packaging?
Chemical and fertilizer plants require:
- Corrosion-resistant robots and stainless-steel components.
- Precise weighing to meet regulatory tolerances.
- Safe handling of hazardous powders.
FAQ
What is the purpose of valve bag automation in packaging systems?
Valve bag automation delivers consistent, high-speed placing, filling and palletizing of valve bags to improve throughput, accuracy and workplace safety.
How does a valve bag filler machine work?
A valve bag filler aligns a bag valve under a discharge spout, then meters material into the bag before the valve closes and seals the bag.
Can valve bag automation integrate with existing machinery?
Yes, conveyors, PLC controls and flexible robot footprints enable seamless integration with current bagging, weighing and palletizing equipment.
What types of products are suitable for valve bag automation?
Common materials include cement, lime, chemicals, fertilizers, sugar, animal feed and minerals — essentially any free-flowing powder or granular bulk product.
How does robotic placement reduce product loss and spillage?
Robots position bags precisely every cycle, eliminating tilt or misalignment that causes spillage and dust exposure.
What challenges do manual valve bag placement processes present?
Manual processes face fatigue, ergonomic injuries, inconsistent fills, material waste, and limited speed, impacting safety and efficiency.
How do labor shortages affect manual valve bagging?
Workforce constraints cause production bottlenecks, increased overtime costs, and reliance on temporary labor, making automation a strategic necessity.
Automating valve bag packaging brings real advantages. With PASCO Systems’ robotic and modular solutions, plants move faster, cut costs, and create safer workplaces. For manufacturers, the question isn’t if automation makes sense — it’s how to design the right system for their line. A customized plan can show exactly where the gains are.